DS - pythonds3 - 8. Graphs and Graph Algorithms
Time and Space Complexity
ref:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/time-complexity-and-space-complexity/
Overview
| 指标 | 定义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | 算法随输入规模增长所需的时间 | O(1), O(N), O(N²) |
| 空间复杂度 | 算法随输入规模增长所需的空间 | O(1), O(N) |
| 常用分析方法 | 只关注输入规模的最高阶项,忽略常数和低阶项 | — |
Many times there are more than one ways to solve a problem with different algorithms and we need a way to compare multiple ways.
- 算法的性能通常从两个角度衡量:
- 时间复杂度(Time Complexity):算法运行所需时间与输入规模(N)的关系。
- 空间复杂度(Space Complexity):算法运行所需内存与输入规模(N)的关系。
这些分析是独立于机器性能的,只与算法逻辑和输入规模有关。
know how much time and resources an algorithm might take when implemented.
- different method
- Independent of the machine and its configuration, on which the algorithm is running on.
- Shows a direct correlation with the number of inputs.
- Can distinguish two algorithms clearly without ambiguity.
⏱ 时间复杂度 Time Complexity
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of an algorithm quantifies the amount of
time takenby an algorithm to run as a function of the length of the input.- Note that the time to run is
a function of the length of the inputand not the actual execution time of the machine on which the algorithm is running on.
- Note that the time to run is
- The valid algorithm takes a finite amount of time for execution. The time required by the algorithm to solve given problem is called
time complexityof the algorithm. It is the time needed for the completion of an algorithm.
To estimate the time complexity, we need to consider the cost of each fundamental instruction and the number of times the instruction is executed.
- In order to calculate time complexity on an algorithm, it is assumed that a constant time
cis taken to execute one operation, and then the total operations for an input length onNare calculated.
📘 示例 1:两个数相加
1
2
3
4
5
6
Algorithm ADD SCALAR(A, B)
//Description: Perform arithmetic addition of two numbers
//Input: Two scalar variables A and B
//Output: variable C, which holds the addition of A and B
C <- A + B
return C
The addition of two scalar numbers requires one addition operation. the time complexity of this algorithm is
constant, soT(n) = O(1). 只执行一次加法操作,因此时间复杂度为O(1)。
📘 示例 2:寻找数组中和为 Z 的一对数
- Consider an example to understand the process of calculation: Suppose a problem is to find whether a pair (X, Y) exists in an array, A of N elements whose sum is Z.
The simplest idea is to consider every pair and check if it satisfies the given condition or not.
- The pseudo-code is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int a[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
cin >> a[i]
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
if(i!=j && a[i]+a[j] == z)
return true
return false
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find a pair in the given
# array whose sum is equal to z
def findPair(a, n, z) :
# Iterate through all the pairs
for i in range(n) :
for j in range(n) :
# Check if the sum of the pair
# (a[i], a[j]) is equal to z
if (i != j and a[i] + a[j] == z) :
return True
return False
# Driver Code
# Given Input
a = [ 1, -2, 1, 0, 5 ]
z = 0
n = len(a)
# Function Call
if (findPair(a, n, z)) :
print("True")
else :
print("False")
# This code is contributed by splevel62.
# Output
False
Assuming that each of the operations in the computer takes approximately constant time, let it be
c. The number of lines of code executed actually depends on the value ofZ. During analyses of the algorithm, mostly the worst-case scenario is considered, i.e., when there is no pair of elements with sum equalsZ. In the worst case,
- N*c operations are required for input.
- The outer loop
iloop runsNtimes.- For each
i, the inner loopjloop runsNtimes. So total execution time isN*c + N*N*c + c. Now ignore the lower order terms since the lower order terms are relatively insignificant for large input, therefore only the highest order term is taken (without constant) which is N*N in this case. Different notations are used to describe the limiting behavior of a function, but since the worst case is taken so big-O notation will be used to represent the time complexity.- 外层循环执行
N次,内层循环也执行N次- 总操作次数:
N × N = N²- 👉 时间复杂度:
O(N²)
📘 示例 3:嵌套循环(N, N/2, N/4…)
1
2
3
4
5
6
count = 0
i = N
while(i > 0):
for j in range(i):
count + = 1
i /= 2
- When i = N, it will run N times.
- When i = N / 2, it will run N / 2 times.
- When i = N / 4, it will run N / 4 times.
- The total number of times count++ will run is
N + N/2 + N/4+...+1= 2 * N. - So the time complexity will be
O(N).
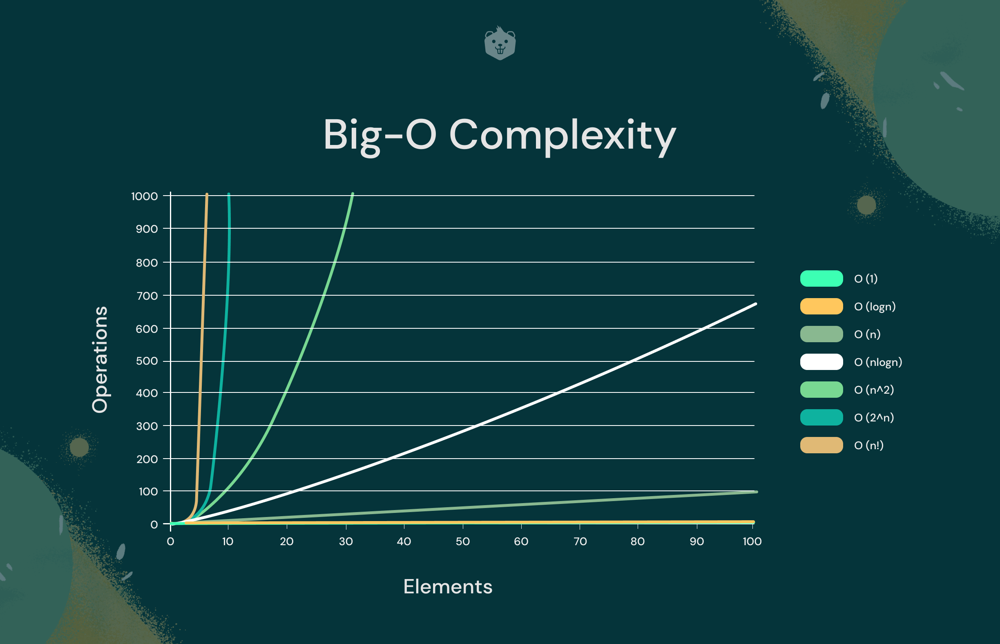
Big-O Notation
O(1) – Constant Time
The runtime does not depend on the input size.
1
2
3
4
// accessing an element in an array by its index is an O(1) operation.
int getElement(int arr[], int index) {
return arr[index]; // O(1)
}
O(log n) – Logarithmic Time
This occurs when the algorithm cuts the problem size in half at each step, such as in binary search.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
int binarySearch(int arr[], int n, int target) {
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (arr[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid - 1;
}
return -1; // O(log n)
}
O(n) – Linear Time
The algorithm’s runtime grows directly proportional to the input size
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// simple loop through an array.
int findMax(int arr[], int n) {
int maxVal = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] > maxVal)
maxVal = arr[i];
}
return maxVal; // O(n)
}
O(n log n) – Linearithmic Time
This complexity is common in efficient sorting algorithms like Merge Sort and Quick Sort.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return;
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, l, m);
mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r);
merge(arr, l, m, r); // O(n log n)
}
O(n^2) – Quadratic Time
The runtime grows quadratically with the input size.
This is typical for algorithms with nested loops, like bubble sort.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
swap(arr[j], arr[j+1]);
}
} // O(n^2)
}
O(2^n) – Exponential Time
This complexity appears in recursive algorithms where the problem branches into multiple subproblems, like the naive Fibonacci implementation.
1
2
3
4
int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); // O(2^n)
}
O(n!) – Factorial Time
Algorithms with this complexity grow rapidly and are generally impractical for large inputs, like the solution to the Traveling Salesman Problem and Print Permutations using brute force.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
vector<int> nums = {1, 2, 3}; // Example vector
void printPermutations(vector<int>& nums) {
do {
for (int num : nums)
cout << num << " ";
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())); // O(!n)
}
general time complexities
| Input Length | Worst Accepted Time Complexity | Usually type of solutions |
|---|---|---|
| 10 -12 | O(N!) | Recursion and backtracking |
| 15-18 | O(2N \* N) | Recursion, backtracking, and bit manipulation |
| 18-22 | O(2N \* N) | Recursion, backtracking, and bit manipulation |
| 30-40 | O(2N/2 \* N) | Meet in the middle, Divide and Conquer |
| 100 | O(N4) | Dynamic programming, Constructive |
| 400 | O(N3) | Dynamic programming, Constructive |
| 2K | O(N2\* log N) | Dynamic programming, Binary Search, Sorting, Divide and Conquer |
| 10K | O(N2) | Dynamic programming, Graph, Trees, Constructive |
| 1M | O(N\* log N) | Sorting, Binary Search, Divide and Conquer |
| 100M | O(N), O(log N), O(1) | Constructive, Mathematical, Greedy Algorithms |
💾 空间复杂度(Space Complexity)
Definition
- 算法执行时所需的内存总量。包括:
- 固定部分:代码、常量、变量等,与输入规模无关。
可变部分:递归栈、动态数据结构,与输入规模相关。
the amount of memory needed for the completion of an algorithm.
Problem-solving using computer requires memory to hold temporary data or final result while the program is in execution. The amount of memory required by the algorithm to solve given problem is called space complexity of the algorithm.
- The space complexity of an algorithm quantifies the amount of space taken by an algorithm to run as a function of the length of the input. Consider an example: Suppose a problem to find the frequency of array elements.
To estimate the memory requirement we need to focus on two parts:
(1) A fixed part: It is independent of the input size. It includes memory for instructions (code), constants, variables, etc.
(2) A variable part: It is dependent on the input size. It includes memory for recursion stack, referenced variables, etc.
📘 示例:计算数组中每个元素出现次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
Algorithm ADD SCALAR(A, B)
//Description: Perform arithmetic addition of two numbers
//Input: Two scalar variables A and B
//Output: variable C, which holds the addition of A and B
C <— A+B
return C
The addition of two scalar numbers requires one extra memory location to hold the result. Thus the space complexity of this algorithm is constant, hence
S(n) = O(1).
The pseudo-code is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
int freq[n];
int a[n];
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
freq[a[i]]++;
}
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to count frequencies of array items
def countFreq(arr, n):
freq = dict()
# Traverse through array elements and
# count frequencies
for i in arr:
if i not in freq:
freq[i] = 0
freq[i]+=1
# Traverse through map and print frequencies
for x in freq:
print(x, freq[x])
# Driver Code
# Given array
arr = [10, 20, 20, 10, 10, 20, 5, 20 ]
n = len(arr)
# Function Call
countFreq(arr, n)
# This code is contributed by Shubham Singh
需要两个长度为 N 的数组 + 常数空间 总空间 =
2N + 1 ≈ O(N)。 📌 辅助空间(Auxiliary Space):指除输入数据外的额外空间。 在上例中,freq[] 是辅助空间,因此辅助空间复杂度为O(N)。

Comments powered by Disqus.