LLM - OWASP Top 10 for LLM
OWASP Top 10 for LLM
Table of contents:
ref:
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02059
- https://neo4j.com/developer-blog/knowledge-graphs-llms-multi-hop-question-answering/
Overview
This undertaking is not a one-time effort but a continuous process, mirroring the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats. With the rapid advancements in LLMs, their potential for both utility and abuse will continue to grow, making the task of security a continually moving target that demands the attention and expertise.
In closing, the quest for robust security measures for LLMs is ongoing.
ensure that the tools are not just powerful and effective, but also
secure and ethically used.
OWASP Top 10 for LLM
The frenzy of interest in Large Language Models (LLMs) following the mass-market pre-trained chatbots in late 2022 has been remarkable.
Businesses, eager to harness the potential of LLMs, are rapidly integrating them into their operations and client-facing offerings. Yet, the breakneck speed at which LLMs are being adopted has outpaced the establishment of comprehensive security protocols, leaving many applications vulnerable to high-risk issues.
The absence of a
unified resource addressing these security concerns in LLMswas evident. Developers, unfamiliar with the specific risks associated with LLMs, were left with scattered resources and OWASP’s mission seemed a perfect fit to help drive safer adoption of this technology.
Who is it for?
- the primary audience is developers, data scientists and security experts tasked with designing and building applications and plug-ins leveraging LLM technologies. aim to provide practical, actionable, and concise security guidance to help these professionals navigate the complex and evolving terrain of LLM security.
The Making of the List
The creation of the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs list was a major undertaking, built on the collective expertise of an international team of nearly 500 experts, with over 125 active contributors. the contributors come from diverse backgrounds, including AI companies, security companies, ISVs, cloud hyperscalers, hardware providers and academia.
Over the course of a month, brainstormed and proposed
potential vulnerabilities, with team members writing up 43 distinct threats. Through multiple rounds of voting, refined these proposals down to a concise list of the ten most critical vulnerabilities. Each vulnerability was then further scrutinized and refined by dedicated sub-teams and subjected to public review, ensuring the most comprehensive and actionable final list.Each of these vulnerabilities, along with common examples, prevention tips, attack scenarios, and references, was further scrutinized and refined by dedicated sub-teams and subjected to public review, ensuring the most comprehensive and actionable final list.
Relating to other OWASP Top 10 Lists
While the list shares DNA with vulnerability types found in other OWASP Top 10 lists, do not simply reiterate these vulnerabilities. Instead, delve into the unique implications these vulnerabilities have when encountered in applications utilizing LLMs.
the goal is to bridge the divide between general application security principles and the specific challenges posed by LLMs. This includes exploring how conventional vulnerabilities may pose different risks or might be exploited in novel ways within LLMs, as well as how traditional remediation strategies need to be adapted for applications utilizing LLMs.
The Future
- This first version of the list will not be the last. expect to update it on a periodic basis to keep pace with the state of the industry. will be working with the broader community to push the state of the art, and creating more educational materials for a range of uses. also seek to collaborate with standards bodies and governments on AI security topics. welcome you to join the group and contribute.
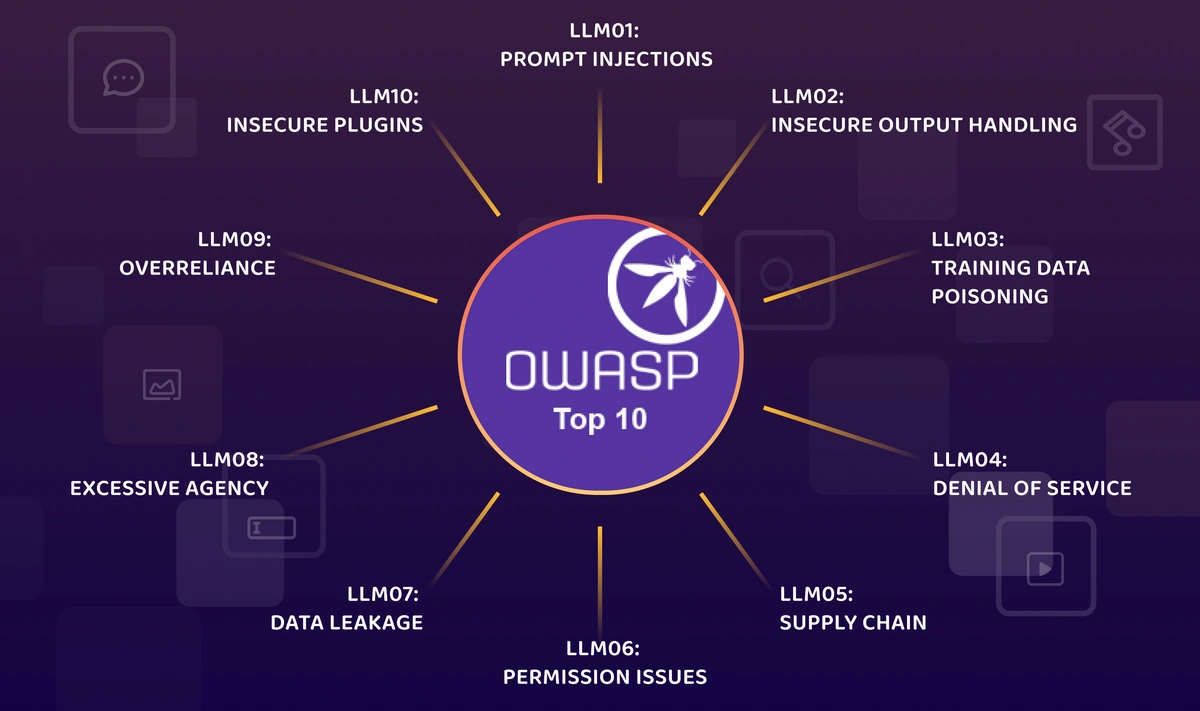
Top 10
LLM01: Prompt Injection
- This manipulates a large language model (LLM) through
crafty inputs, causing unintended actions by the LLM. Direct injections overwrite system prompts, while indirect ones manipulate inputs from external sources.
LLM02: Insecure Output Handling
- This vulnerability occurs when an
LLM output is accepted without scrutiny, exposing backend systems. Misuse may lead to severe consequences like XSS, CSRF, SSRF, privilege escalation, or remote code execution.
LLM03: Training Data Poisoning
- This occurs when
LLM training data is tampered, introducing vulnerabilities or biases that compromise security, effectiveness, or ethical behavior. Sources include Common Crawl, WebText, OpenWebText, & books.
LLM04: Model Denial of Service
- Attackers cause
resource-heavy operations on LLMs, leading to service degradation or high costs. The vulnerability is magnified due to the resource-intensive nature of LLMs and unpredictability of user inputs.
LLM05: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- LLM application lifecycle can be
compromised by vulnerable components or services, leading to security attacks.Using third-party datasets, pre-trained models, and pluginscan add vulnerabilities.
LLM06: Sensitive Information Disclosure
- LLM’s may
inadvertently reveal confidential data in its responses, leading to unauthorized data access, privacy violations, and security breaches. It’s crucial to implement data sanitization and strict user policies to mitigate this.
LLM07: Insecure Plugin Design
- LLM plugins can have insecure inputs and insufficient access control. This lack of application control makes them
easier to exploit and can result in consequences like remote code execution.
LLM08: Excessive Agency 过度代理
- LLM-based systems may undertake actions leading to unintended consequences. The issue arises from excessive functionality, permissions, or autonomy granted to the LLM-based systems.
LLM09: Overreliance 过度依赖
Systems or people overly depending on LLMs without oversight may face
misinformation, miscommunication, legal issues, and security vulnerabilities due to incorrect or inappropriate content generated by LLMs.LLM10: Model Theft
- This involves
unauthorized access, copying, or exfiltration of proprietary LLM models. The impact includes economic losses, compromised competitive advantage, and potential access to sensitive information.
- This involves
Comments powered by Disqus.