AWS - IdenAccessManage - IDMS
IDMS
Enhances Metadata Service Security with IMDSv2
AWS would continue to support the previous version of the instance metadata service.
- Administrators may choose to disable IMDSv1 completely.
- AWS has introduced a new Cloudwatch metric (MetadataNoToken) to track IMDSv1 requests .
- Obviously one needs to use this metric and ensure that no instances are using IMDSv1 before disabling it altogether.
IMDS
Instance Metadata Service (IMDS)
- 实例元数据服务
- IMDS provides a convenient way to access metadata about a running EC2 instance such as host name, network config, security groups etc.
- IMDS 的位置是基於 APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) 的 169.254.169.254 位置
- The service runs on a link-local IP address
- link-local IP address is unique to every single instance. https://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/
- 提供有关实例的信息以及与其关联的各种参数,例如
- 在启动时指定的用户数据。
- Instance-Id、AMI、Region 等等狀態。
- IMDSv1 将凭证存储在端点中
- 可以检索这些凭证,然后使用这些凭证通过 AWS CLI 执行操作。
- 在凭证被渗透的情况下,这可能是毁灭性的。
- 因此引入了 IMDSv2 来阻止针对滥用元数据端点的各种攻击。
- IMDSv2 使用会话不将会话令牌作为信息存储在端点本身中,
- 因此在后续调用中生成令牌后无法检索令牌。
One of the most important use-cases for IMDS is to
- allow applications running on EC2 instances to access AWS resources.
- In a world without IMDS
- have to use hard-coded API keys to enable communication between AWS services and resources.
- The metadata service solves this problem with “temporary security credentials”.
- These credentials are rotated on a regular basis and managed by the AWS STS service.
Security Concerns around IMDSv1
- The metadata service was designed to be accessible only from within the instance. However, there is no additional access control to prevent unauthorized access from a compromised application running on the EC2 instance itself.
- Application vulnerabilities such as Server Side Request Forgery, XML External Entity Injection etc. may be exploited to gain access to the metadata service.
one such example.
- Capital One Data Breach:
- This behavior has been exploited numerous times in the past few years by hackers.
- The attack pattern is to gain access to the metadata service by exploiting a vulnerable app within EC2.
- This in turn exposes the temporary security credentials.
- The credentials make it trivial to access AWS resources that share a trust relationship with the affected EC2 instance.
- The Capital One security breach which affected more than 100 million people in North America, was the most recent example of this exploit. AWS has faced a lot of criticism for not addressing this issue from the security community in general. Finally, they have introduced a successor to the metadata service which uses defense in depth to improve the overall security posture.
IMDSv2
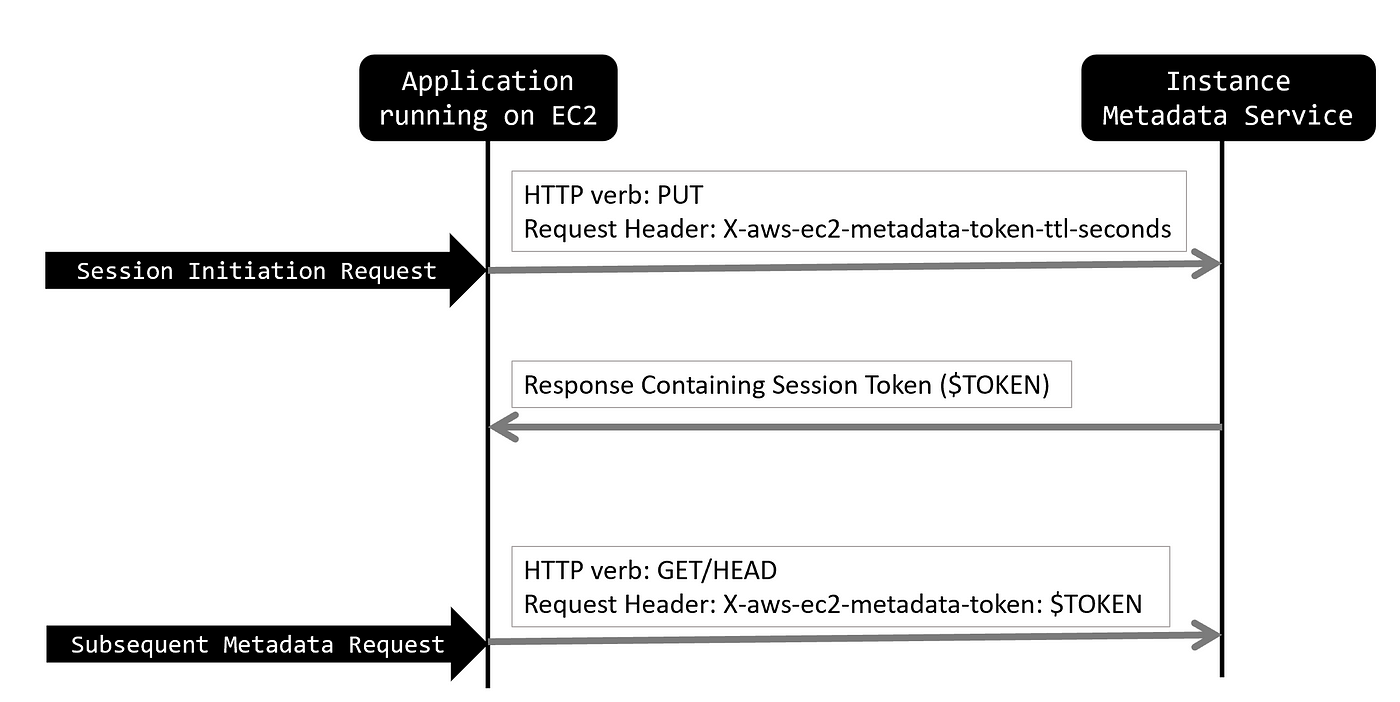
- The version 2 of the Instance Metadata Service uses session based authentication.
- An app running inside the EC2 instance can start a session by sending an HTTP PUT request to IMDSv2.
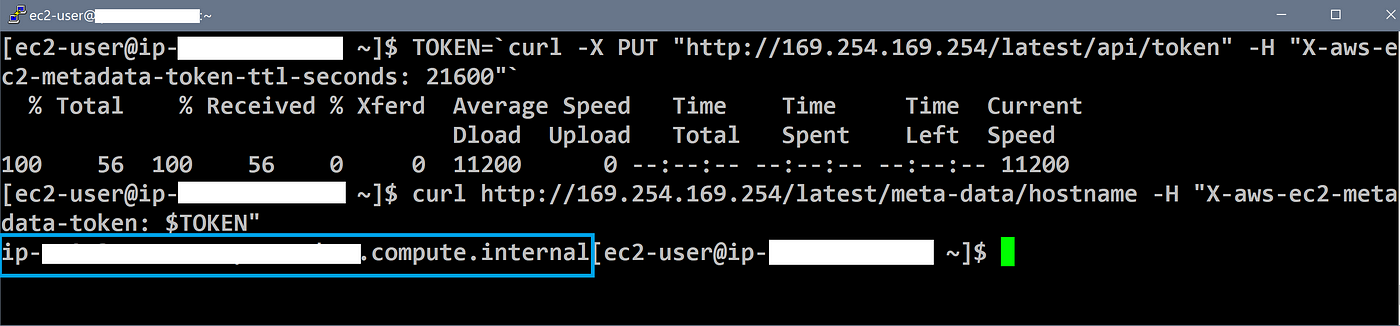
Obtain Instance host name Using IMDSv2
- The first command specifies the HTTP verb:
PUT. An additional header is used to specify the time to live (TTL) value in seconds. Output of the first command is stored in a variable named “TOKEN”. In this case the token would be valid for 6 hours (21600 seconds). The request header is mandatory to obtain a valid session token and 21600 seconds is the maximum TTL value allowed. - The subsequent requests for metadata must contain the token in the request header. Refer to the screenshot below to understand how you may access the IMDSv2 on your EC2 instances.
1
2
3
4
5
TOKEN=`curl PUT "https://169.254.169.254/latest/api/token" \
-X \
-H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21600"`
curl https://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/profile \
-H “X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN”
changes result in a more secure version of the metadata service.
- PUT Request for session initiation:
- Mis-configured open web application firewalls or reverse proxies may expose the metadata service outside the EC2 instance.
- but these services often do not support
PUT methodwhich ensure safety of the IMDSv2. - The session oriented approach involves the
PUT methodand the mandatory request header (X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds). - This protects against exploitation using SSRF/XXE vulnerabilities present inside the EC2 instance.
- X-Forwarded-For header not allowed:
- An open reverse proxy may allow the PUT request.
- However requests passed through a proxy would contain the “X-Forwarded-For” header. Such requests are rejected by the IMDSv2 and the token is not issued.
- IP Packet TTL set to “1”:
- This is a network level security control which ensures that the HTTP response containing the secret token would not travel outside the EC2 instance.
- The TTL field in the IP packet sets a limit on the number of network hops that can be taken by the packet.
- The value is reduced by one on every hop.
- Even if an attacker is able to to bypass all the other protections, this would ensure that the token would not travel outside the EC2 instance and the packet would be dropped as soon as it leaves the EC2 instance.
IP Packet TTL
但是在 Kubernetes 的網路設計中 Pod 要訪問 IMDSv2 需要經過多個虛擬網卡轉譯至少需要 hop 2 以上才能到達,所以 hop 上限至少也要 2 以上
- 這個在 Amazon EKS Managed node group 預設就是採用 hop 2
- 但是對於 Self-managed node 除非是用 eksctl 就要自己設定 hop 2。
- CLI 2. ```bash $ aws ec2 describe-instances
–instance-id i-0c48d5aac6576a19f
| grep HttpPutResponseHopLimit“HttpPutResponseHopLimit”: 1,
$ aws ec2 modify-instance-metadata-options
–instance-id i-0c48d5aac6576a19f
–http-tokens required
–http-endpoint enabled
–http-put-response-hop-limit 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2. 用 Auto Scaling Group 來建立 Self-managed node
1. hop limit 可以在 Launch template 內找到設定 Metadata response hot limit 參數
## 使用 AWS CLI 为新实例启用 IMDSv2
```bash
aws ec2 run-instances \
--image-id sss \
--metadata-options "HttpEndpoint=enabled,HttpTokens=required"
# 运行以下 AWS CLI 命令以修改实例并启用 IMDSv2:
aws ec2 modify-instance-metadata-options \
--instance-id zzz \
--http-tokens required \
--http-endpoint enabled
# After you've created a token, you can reuse it until it expires. In the following example command, which gets the ID of the AMI used to launch the instance, the token that is stored in $TOKEN in the previous example is reused.
[ec2-user ~]$ curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" -v https://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ami-id
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
Comments powered by Disqus.