GCP - Network connection
- Hybrid cloud and VPC connection
- GCP -Cloud Interconnect and Peering
Hybrid cloud and VPC connection
VPCs belong to GCP projects if the company has several GCP projects and the VPCs need to talk to each other
VPC sharing and peering
VPC connection
Shared VPC
- to share a VPC network, or individual subnets, with other GCP projects
- share a VPC network from one project (called a host project) to other projects in the Google Cloud organization.
- to use the full power of IAM
- control who and what in one project can interact with a VPC in another
- grant access to entire Shared VPC networks or select subnets by specific IAM permissions.
- provide centralized control over a common network while maintaining organizational flexibility.
- Shared VPC is especially useful in large organizations.
VPC Network Peering
peering relationship between two VPCs to exchange traffic
to interconnect networks in GCP projects
VPC Network Peering lets you build software as a service (SaaS) ecosystems in Google Cloud, making services available privately across different VPC networks, whether the networks are in the same project, different projects, or projects in different organizations.
- With VPC Network Peering, all communication happens by using internal IP addresses.
- Subject to firewall rules, VM instances in each peered network can communicate with one another without using external IP addresses.
- Peered networks
automatically exchange subnet routes for private IP address ranges.- VPC Network Peering lets you configure whether the following types of routes are exchanged:
- Subnet routes for privately re-used public IP ranges
- Custom static and dynamic routes
- Network administration for each peered network is unchanged:
- IAM policies are never exchanged by VPC Network Peering.
- For example, Network and Security Admins for one VPC network do not automatically get those roles for the peered network.
Hybrid cloud connection
- interconnect their networks to Google VPCs
- such as on-premises networks or their networks in other clouds.
Virtual Private Network
connect the VPC network to the physical, on-premises network or another cloud provider by using a secure virtual private network.
- Virtual Private Network connection over the internet using the IPSEC protocol.
- Cloud Router
- simple way to let a VPN into Google VPC continue to work in spite of routing changes,
- Cloud Router lets their networks and the Google VPC exchange route information over the VPN using the Border Gateway Protocol.
- example
- add a new subnet to the Google VPC,
- the on-premises network will automatically get routes to it.
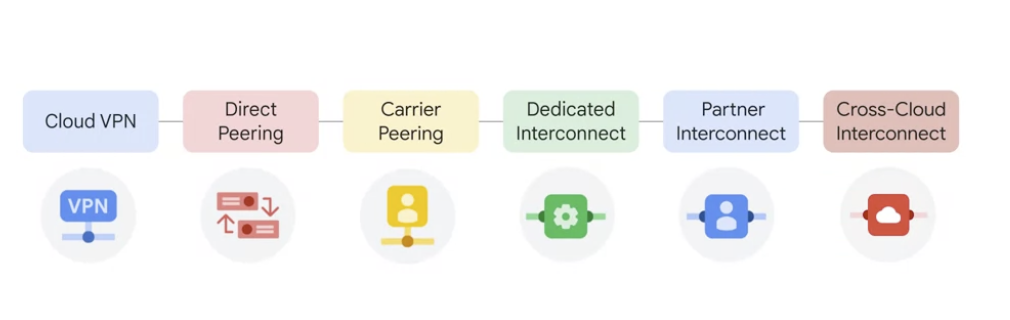
Direct Peering
- don’t want to use the internet
- either because of security concerns or need more reliable bandwidth.
- peering with Google using Direct Peering.
- putting a router in the same public data center as a Google point of presence and exchanging traffic.
- Google has more than 100 points of presence around the world.
- Customers who aren’t already in a point of presence can contract with a partner in the carrier peering program to get connected.
- One downside:
- it isn’t covered by a Google service level agreement.
- Customers who want the highest uptimes for their interconnection with Google should use Dedicated Interconnect
- If these connections have topologies that meet Google’s specifications, they can be covered by up to a 99.99 percent SLA.
- These connections can be backed up by a VPN for even greater reliability.
Dedicated Interconnect
- customers get one or more direct private connections to Google.
- highest uptimes for their interconnection with Google
- connect the VPC network to the on-premises network by using a high speed physical connection.
Private Google Access
enable Private Google Access for a subnet
- instances in a subnet of a VPC network can communicate with Google APIs and services by using private IP addresses instead of external IP addresses.
GCP -Cloud Interconnect and Peering
different Cloud Interconnect and Peering services available to connect the infrastructure to Google’s network.
- Direct Peering, Carrier Peering, Dedicated Interconnect, and Partner Interconnect
.
- Cloud VPN
- Google also offers its own Virtual Private Network service
- uses the public Internet
- but traffic is encrypted and provides access to internal IP addresses.
- Cloud VPN is a useful addition to Direct Peering and Carrier Peering.
- Dedicated connections
- provide a direct connection to Google’s network.
- shared connections
- provide a connection to Google’s network through a partner.
- Layer two connections
- use a VLAN that pipes directly into the GCP environment, providing connectivity to internal IP addresses in the RFC 1918 address space.
- Layer three connections
- provide access to G Suite services, YouTube and Google Cloud APIs using public IP addresses.
Layer three connections: VPN
1. Cloud VPN
- securely connects the on-premise network to the GCP VPC network through an IPSec VPN tunnel.
- Traffic traveling between the two networks is encrypted by one VPN gateway. Then decrypted by the other VPN gateway.
- protects the data as it travels over the public internet.
- That’s why Cloud VPN is useful for low volume data connections.
- managed service, SLA of
99.9%service availability - supports site to site VPN static and dynamic routes, and IKEv1 and IKEv2 ciphers.
- Cloud VPN doesn’t support new cases where a client computers need to dial in to a VPN using client VPN software.
- Also, dynamic routes are configured with Cloud Router
a VPN connection between the VPC and on-premise network.
- the VPC network has subnets in US-east one and US-west one.
- With GCP resources in each of those regions.
- These resources are able to communicate using internal IP addresses\
- routing within a network is automatically configured, as that firewall rules allow it.
- to connect to the on-premise network and its resources
- configure the
Cloud VPN gateway,on-premise VPN gatewayand toVPN tunnels.
- configure the
- The Cloud VPN gateway
- a regional resource, uses regional external IP address.
- the on-premise VPN gateway
- can be a physical device in the data center or a physical or software based VPN offering in another Cloud providers network.
- This VPN gateway also has an external IP address.
- A VPN tunnel
- A VPN tunnel then connects the VPN gateways
- and serves as the virtual medium through which encrypted traffic is passed.
- to create a connection between two VPN gateways, two VPN tunnels is needed.
- Each tunnel defines the connection from the perspective of its gateway and traffic can only pass when the pair of tunnels established.
- Now, one thing to remember when using Cloud VPN is that the maximum transmission unit, MTU for the on-premises VPN gateway cannot be greater than
1,460 bytes.- because of the encryption and encapsulation of packets.
Cloud VPN gateway
| Classic VPN | High-availability (HA) VPN |
|---|---|
| Supports dynamic routing and static routing | Supports dynamic routing (BGP) only |
| No high availability | high availability (99.99 SLA, within region) |
Classic VPN
- support static and dynamic routes.
dynamic routes
need to configure Cloud Router.
Cloud Router
- manage routes from Cloud VPN tunnel using border gateway protocol, BGP .
- routing method
- allows for routes to be updated and exchanged without changing the tunnel configuration.
For example
- two different regional subnets in a VPC network
- The on-premise network has 29 subnets
- the two networks are connected through
Cloud VPN tunnels.
To automatically propagate network configuration
- changes the VPN tunnel uses Cloud Router to establish a
BGP sessionbetween the VPC and the on-premise VPN gateway which must support BGP. - The new subnets are then seamlessly advertised between networks.
- This means that instances in the new subnets can start sending and receiving traffic immediately
- To set up BGP
- an additional IP address has to be assigned to each end of the VPN tunnel.
- These two IP addresses must be link-local IP addresses Belonging to the IP address range
169.254.0.0/16 - These addresses are not part of IP address space of either network
- are used exclusively for establishing a BGP session.
HA VPN. Alternative Cloud VPN Gateway
- a high availability Cloud VPN solution
- securely connect the on-premises network to the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network through an
IPsec VPN connectionin a single region - HA VPN provides an SLA of
99.99%service availability.
Layer three connections: Peering
Direct Peering and Carrier Peering
- all provide public IP address access to all of Google’s services.
- The main differences are capacity and the requirements for using a service.
- Direct Peering has a capacity of 10 Gbps per link and requires you to have a connection in a GCP edge point of presence.
- Carrier Peerings, capacity and requirements depending on the service provider that you work with.
2. Direct Peering
- useful when you require access to Google and Google cloud properties.
- Google allows you to establish a direct peering connection between the business network and Google’s.
will be able to exchange internet traffic between the network and Google ’s at one of the Googles broad reaching edge network locations.
- Direct Peering
- exchanging BGP route between Google and peering entity.
- use it to reach all the Google services, including the full suite of Google cloud platform products.
- does not have an SLA
.
- In order to use direct peering
- need to satisfy the peering requirements
- GPS edge
Points of Presenceor PoPs are where Google’s network connects to the rest of the internet via peering. - PoPs are present on over 90 Internet exchanges and at over 100 interconnection facilities around the world.
3. Carrier Peering
nowhere near one of these locations, consider Carrier Peering.
If you require access to Google public infrastructure and cannot satisfy Google’s peering requirements, you can connect with a
Carrier Peering partner.Work directly with the service provider to get the connection you need and to understand the partners requirements.
- does not have an SLA
.
Layer two connections: Dedicated and Partner Interconnect
Dedicated and Partner Interconnect
- All of these options provide internal IP address access between resources in the on-premise network and in the VPC network.
- The main differences are the connection capacity and the requirements for using a service.
IPsec VPN tunnels
- IPsec VPN tunnels
- Cloud VPN offers
- capacity of 1.5-3 Gbps per tunnel
- require a VPN device on the on-premise network.
- The 1.5 Gbps capacity applies to the traffic that traverses the public Internet, and the 3 Gbps capacity applies to the traffic that is traversing a direct peering link.
- can configure multiple tunnels if you want to scale this capacity.
4. Dedicated Interconnect
- Dedicated Interconnect
- capacity of 10 Gbps per link
- requires a connection in a Google-supported co-location facility.
- You can have up to eight links to achieve multiples of 10 Gbps, but 10 Gbps is the minimum capacity. As of this recording, there is a Beta feature that provides 100 Gbps per link with a maximum of two links.
provides direct physical connections between the on-premise network and Google's network .
allows for direct, private connections to Google with high uptimes and can be backed up by a VPN for greater reliability.
- enables to transfer large amount of data between networks
- more cost-effective than purchasing additional bandwidth over the public Internet.
- Dedicated Interconnect
- allow user traffic from the on-premises network to reach GCP resources on the VPC network and vice-versa.
- can be configured to offer a 99.9% or a 99.99% uptime SLA.
- to use Dedicated Interconnect
- provision a cross-connect between the Google network and the own router in a common co-location facility,
- To exchange routes between the networks, configure a BGP session over the Interconnect between the
Cloud routerand theon-premise router. - the network must physically meet Google’s network in a supported co-location facility.
5. Partner Interconnect
- Partner Interconnect
- capacity of 50 Mbps to 10 Gbps per connection,
- requirements depend on the service provider.
provides connectivity between the on-premises network and the VPC network through a supported service provider .
This is useful if the data center is in the physical location that cannot reach a Dedicated Interconnect co-location facility or if the data needs don’t warrant a Dedicated Interconnect.
In order to use Partner Interconnect, work with a supported service provider to connect the VPC and on-premise networks.
These service providers have existing physical connections to Google’s network that they make available for their customers to use.
After you establish connectivity with the service provider, you can request a Partner Interconnect connection from the service provider,
then establish a BGP session between the
Cloud routerandon-premise routerto start passing traffic between the networks.
- can be configured to offer a 99.9% or a 99.99% uptime SLA between Google and the service provider.
recommendation start with VPN tunnels. When need enterprise-grade connection to GCP, switch to Dedicated Interconnect or Partner Interconnect, depending on the proximity to a co-location facility and the capacity requirements.
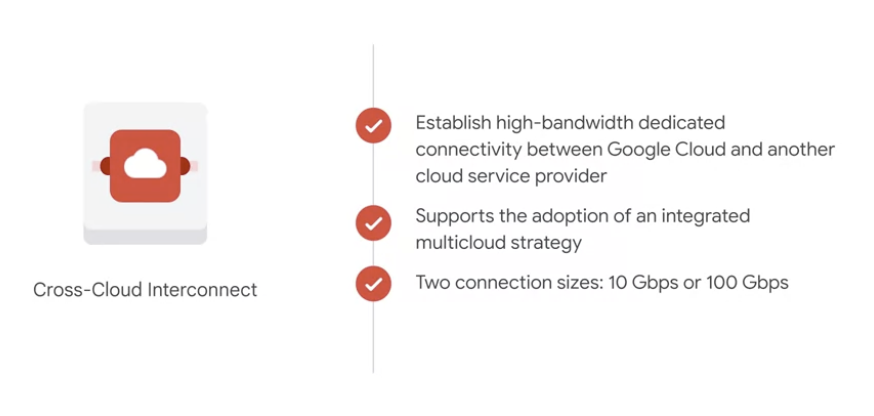
5. Cross-Cloud Interconnect
helps establish high-bandwidth dedicated connectivity between Google Cloud and another cloud service provider .
It supports an integrated multicloud strategy and offers reduced complexity, site-to-site data transfer, and encryption.
connections are available in two sizes: 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps.
.






















Comments powered by Disqus.