GCP - Google Cloud Computing Solutions
Google Cloud Computing Solutions
Cloud Computing
5 fundamental attributes, definition of cloud
- on-demand and self-service
- automated interface and get the processing power, storage, and network they need with no human intervention.
- broad network access
- resources are accessible over a network from any location.
- Resource pooling
- Providers allocate resources to customers from a large pool,
- allowing them to benefit from economies of scale.
- Customers don’t have to know or care about the exact physical location of these resources.
- Rapid elasticity
- Resources themselves are elastic.
- Customers who need more resources can get them rapidly,
- when they need less they can scale back.
- Measured service
- customers pay for only what they use or reserve as they go.
- stop using resources, stop paying.
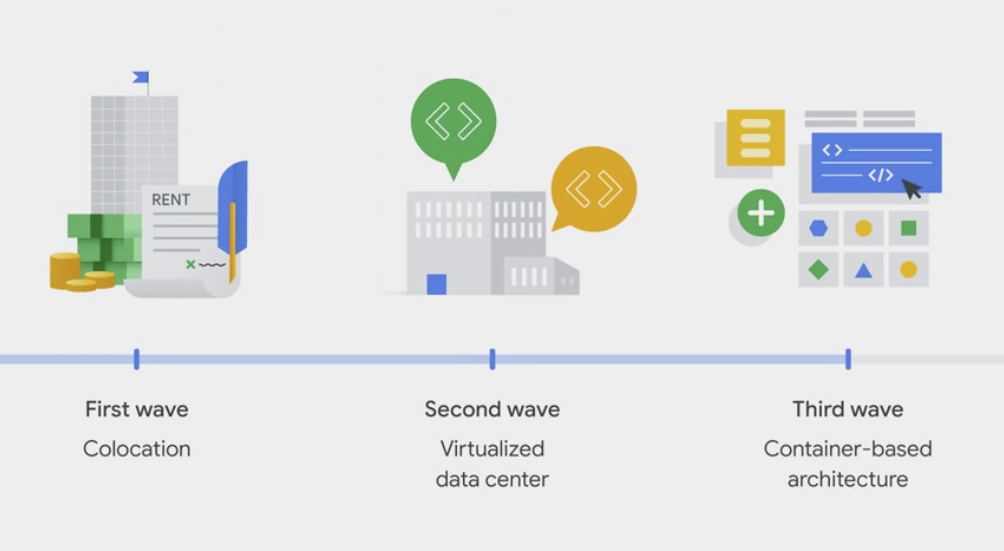
Cloud Compute trend
The trend towards cloud computing started with colocation, which allowed users to rent physical space instead of investing in data center real estate.
Virtualized data centers emerged as the second wave of cloud computing, where physical components were replaced with virtual devices.
Google realized that the virtualization model was limiting their ability to innovate, so they switched to a container-based architecture.
Google Cloud Computing Solutions
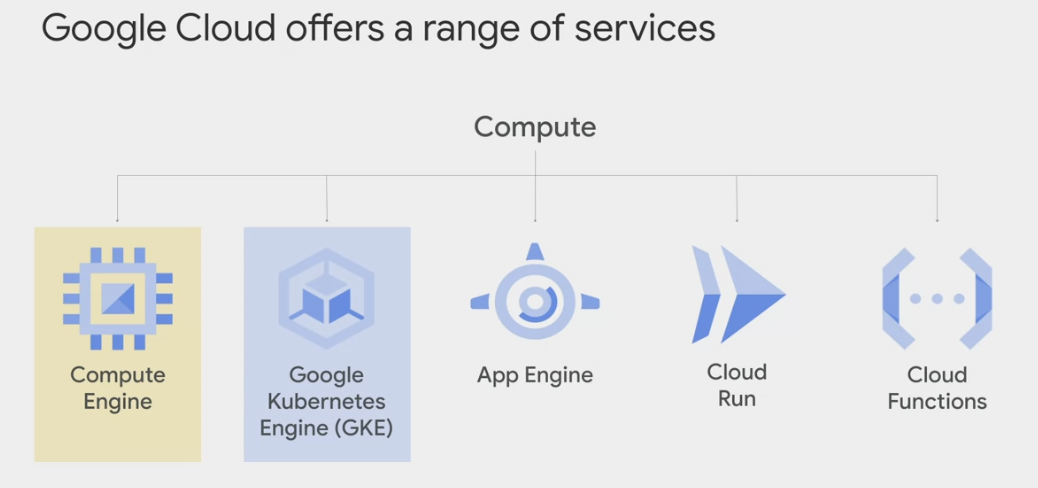
GCP products that provide the compute infrastructure for applications
Compute type
compare
IaaS vs PaaS vs Serverless vs SaaS
IaaS
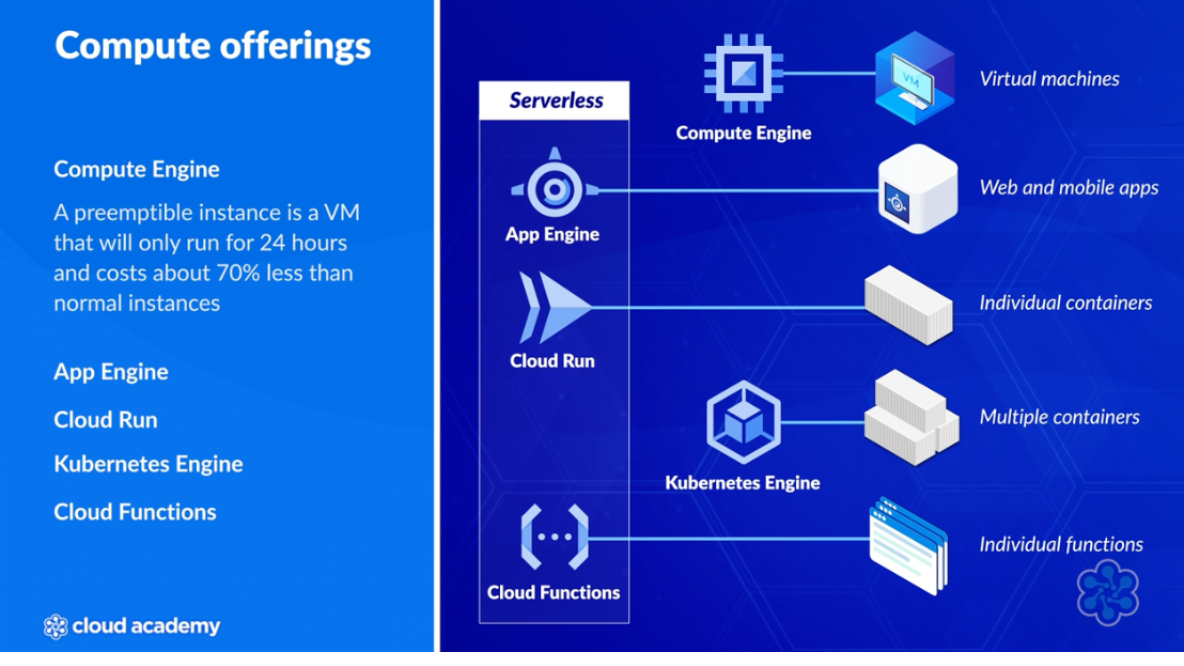
Compute Engine
- Compute Engine
- detailed page
- Infrastructure as a Service
- A managed environment for deploying virtual machines
- Fully customizable VMs
- Compute Engine offers virtual machines that run on GCP
- create and run virtual machines on Google infrastructure.
- run virtual machines on demand in the Cloud.
- select predefined VM configurations
- create customized configurations
- no upfront investments
- run thousands of virtual CPUs on a system that is designed to be fast and to offer consistent performance.
- use case
:
- have complete control over your infrastructure
- maximum flexibility
- for people who prefer to manage those server instances themselves.
- customize operating systems and even run applications that rely on a mix of operating systems.
- best option when other computing options don’t support your applications or requirements
- easily lift and shift your on-premises workloads into GCP without rewriting the applications or making any changes.
- have complete control over your infrastructure
PaaS
App Engine
- App Engine
- detailed page
- Platform as a Service
- fully managed serverless application framework.
- deploy an application on App Engine
- hand App Engine the code
- and the App Engine service takes care of the rest.
- focus on code and run code in the Cloud
- without worry about infrastructure.
- focus on building applications instead of deploying and managing the environment.
- Google deal with all the provisioning and resource management.
- no worry about building the highly reliable and scalable infrastructure
- zero server management or configuration deployments for deploying applications
- The App Engine platform manages the hardware and networking infrastructure for the code.
- deploy an application on App Engine
- provides built-in services that many web applications need.
- code the application to take advantage of these services and App Engine provides them.
NoSQL databases, in-memory caching, load balancing, health checks, loggingand away to authenticate users.- could also
run container workloads. Stackdriver monitoring, logging, and diagnostics- such as debugging and error reporting are also tightly integrated with App Engine.
- use Stackdriver’s real time debugging features to analyze and debug your source code.
- Stackdriver integrates with tools such as Cloud SDK, cloud source repositories, IntelliJ, Visual Studio, and PowerShell.
- App Engine also supports
version control and traffic splitting.
- scale the application automatically in response to the amount of traffic it receives.
- only pay for those resources you use.
- no servers to provision or maintain.
- App Engine offers two environments:
- standard and flexible
- App Engine supports popular languages like Java and Node.js, Python, PHP, C#, .NET, Ruby, and Go.
- use case
:
- suited for applications where the workload is highly variable or unpredictable
- web applications and mobile backend.
- websites, mobile apps, gaming backends,
- present a RESTful API to the Internet
- an application program interface
- resembles the way a web browser interacts with the web server.
- RESTful APIs are easy for developers to work with and extend.
- And App Engine makes them easy to operate
Serverless
Cloud Function
- Cloud Function
- functions as a Service
- A managed serverless platform/environment for deploying event-driven functions
- an event-driven, serverless compute service
- for simple single purpose functions that are attached to events.
- It executes the code in response to events,
- whether those occur once a day or many times per second.
- create single-purpose functions that respond to events without servers or runtime binaries.
- just write code in JavaScript for a Node.js environment that GCP provides
- upload the code written in JavaScript or Python, or Go
- configure when it should fire
- setting up a Cloud Function works.
- choose which events you care about.
- triggers: For each event type, you tell Cloud Functions you’re interested in it.
- attach JavaScript functions to the triggers.
- and then GCP will automatically deploy the appropriate computing capacity to run that code.
- the functions will respond whenever the events happen.
- Google scales resources as required, but you only pay for the service while the code runs.
- no pay for servers
- charged for the time that the code/functions runs.
- For each function, invocation memory and CPU use is measured in the 100 millisecond increments, rounded up to the nearest increment.
- provides a perpetual free tier.
- So many cloud function use cases could be free of charge.
- the code is triggered within a few milliseconds based on events.
- can trigger on events in Cloud Storage, Cloud Pub/Sub,
- file is uploaded to Google cloud storage
- or a message is received from Cloud Pub/Sub.
- or in HTTP call
- triggered based on HTTP endpoints define,
- and events in the fire based mobile application back end.
- can trigger on events in Cloud Storage, Cloud Pub/Sub,
to enhance existing applications without having to worry about scaling.
These servers are automatically scaled and are deployed from highly available and a fault-tolerant design.
- Files uploaded into the GCS bucket can be processed in real time.
- the data can be extracted, transformed and loaded for querying in analysis.
- intelligent applications
- such as virtual assistance, chat bots
- video or image analysis, and sentiment analysis.
- use cases
- used as part of a microservices application architecture.
- Some applications, especially those that have microservices architecture, can be implemented entirely in Cloud Functions.
- build symbols, serverless,
- mobile IoT backends
- integrate with third party services and APIs.
- used as part of a microservices application architecture.
container - Stateless
Cloud Run
- Cloud Run
- serverless
- builds, deploys, and manages modern stateless workloads.
- can build the applications in any language using whatever frameworks and tools
- deploy them in seconds without manage and maintain the server infrastructure.
- distracts way all the infrastructure management
- such as provisioning, configuring, managing those servers
- only focus on developing applications.
- run request or event driven stateless workloads
- without having to worry bout servers.
- automatically scales up and down from zero
- depending upon traffic almost instantaneously
- no worry about scale configuration.
- pay for only the resources used
- calculated down to the nearest 100 milliseconds.
- no pay for those over provisioned resources.
- gives the choice of running the containers
- with fully managed or in the own GKE cluster.
- deploy the stateless containers with a consistent developer experience to a fully managed environment or to the own GKE cluster.
- This common experiences enabled by Knative
- Cloud Run is built on Knative
- an open source Kubernetes based platform.
- an open API and runtime environment built on top of Kubernetes.
- Cloud Run is built on Knative
- gives the freedom to move the workloads across different environments and platforms,
- either fully managed on GCP, on GKE
- or anywhere a Knative runs.
- enables you to deploy stateless containers
- that listen for requests or events delivered via HTTP requests.
- use case:
- build your applications in any language using whatever frameworks and tools you wish and deploy them in seconds without having to manage and maintain that server infrastructure.
container - Hybrid
GKE Kubernetes Engine
- GKE Kubernetes Engine
- detailed page
- A managed environment for deploying containerized applications
- to run containerized applications on a Cloud environment that Google Cloud manages for you under the administrative control.
- containerization, a way to package code that’s designed to be highly portable and to use resources very efficiently.
- Kubernetes, a way to orchestrate code in those containers.
- use case
:
- containerized applications
- cloud-native distributed systems
- and hybrid applications
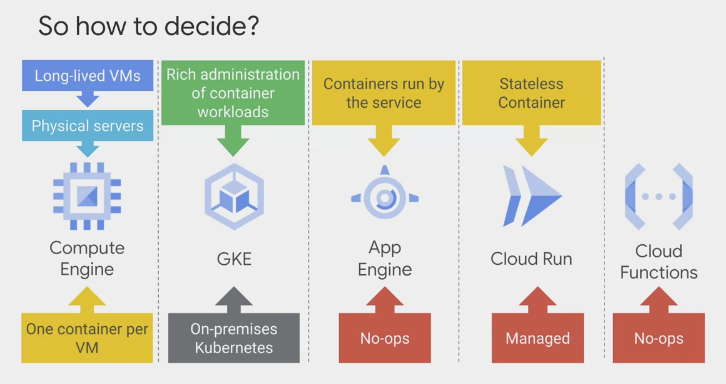
which compute service to you adopt
- compute engine
- running applications on physical server hardware
- running applications in long-lived virtual machines in which each VM is managed and maintained
- moving to compute engine is the quickest GCP services for getting the applications to the cloud.
What do you want to to think about operations at all? Well, App Engine and Cloud Functions are good choices.
- Containerization is the most efficient, importable way to package you an application.
The popularity of containerization is growing very fast.
- both Compute Engine and App Engine can launch containers for you.
- Compute Engine
- accept the container image and launch a virtual machine instance that contains it.
- use Compute Engine technologies to scale and manage the resulting VM.
- App Engine flexible environment
- accept the container image and then run it with the same No-ops environment that App Engine delivers for code.
- Compute Engine
- GKE:
- if you’re already running Kubernetes in the on-premises data centers
- you’ll be able to bring along both the workloads and the management approach.
- want more control over the containerized workloads than what App Engine offers
- And denser packing than what Compute Engine offers
- The Kubernetes paradigm of container orchestration is incredibly powerful, and its vendor neutral, and a abroad and vibrant community is developed all around it.
- Using Kubernetes as a managed service from GCP saves you work and let’s you benefit from all the other GCP resources too.
- if you’re already running Kubernetes in the on-premises data centers
- Cloud Run
- run stateless containers on a managed compute platform.
















Comments powered by Disqus.