GCP - Database
Database
basic
- Cloud Storage
- if you need to store immutable blobs larger than 10 megabytes , such as large images or movies.
- provides petabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 5 terabytes per object.
Cloud SQL or Spanner
if you need full SQL support for an online transaction processing system.
Cloud SQL provides up to 64 terabytes, depending on machine type, and Spanner provides petabytes. Cloud SQL is best for web frameworks and existing applications, like storing user credentials and customer orders.
Spanner if you need horizontal scalability , not just through read replicas
Firestore
- if you need massive scaling and predictability together with real time query results and offline query support.
- provides terabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 1 megabyte per entity.
- best for storing, syncing, and querying data for mobile and web apps .
Bigtable
- if you need to store a large number of structured objects.
- Bigtable doesn’t support SQL queries, nor does it support multi-row transactions.
- provides petabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 10 megabytes per cell and 100 megabytes per row.
- best for analytical data with heavy read and write events , like AdTech, financial, or IoT data.
relational database services
- use a database schema to help your application keep your data consistent and correct.
- Another feature of relational database services that helps with the same goal - transactions.
- application can designate a group of database changes as all or nothing.
- Either they all get made, or none do.
- Without database transactions
- online bank wouldn’t be able to offer you the ability to move money from one account to another.
- What if,
- after subtracting $10,000 from one of your accounts,
- some glitch prevented it from adding that 10,000 to the destination account?
- Your bank would have just misplaced $10,000.
NoSQL
- Datastore is best for
semi-structured application data that is used in app engine application. - Bigtable is best for
running large analytical workloads. - Firestore is ideal for b
uilding client-side mobile and web applications. - Firebase Realtime Database is best for
syncing data between users in real time, such as for collaboration apps. Memorystore is an in-memory datastore that’s typically used to
speed up applications by caching frequently requested data.- Cloud Bigtable
NoSQL- store large amount of structured objects
- with lookups based on a single key
- does not support SQL’s queries
- does not support multi-row transactions.
- provides
petabytesof capacity - maximum unit size of 10 megabytes per cell and 100 megabytes per row.
- use case
- best for analytical data with heavy read/write events
- like AdTech, Financial or IoT data.
- devices with sensors and need to stream huge amounts of data from these devices to a storage option in the cloud
- Cloud Storage
Blobstore- provides
petabytesof capacity - maximum unit size of five terabytes per object.
- often the ingestion point for data being moved into the cloud
- is frequently the long-term storage location for data
- use case:
- best for structured and unstructured, binary or object data
- store immutable blobs larger than 10 megabytes
- such as large images, movies, large media files and backups.
- application that transcodes large video files.
- Immutable binary objects
- and new versions overwrite old unless
- provides
- Cloud SQL
Relational- full SQL support for an online transaction processing
- provides
terabytesof capacity - use case:
- best for web frameworks and in existing applications
- like storing user credentials and customer orders.
- Cloud Spanner
Relational- full SQL support for an online transaction processing system.
- provides
petabytes. - application needs to store data with strong transactional consistency, and want seamless scaling up
- use case:
- If Cloud SQL does not fit the requirements as need horizontal scalability not just through read replicas
- best for large scale database applications that are larger than two terabytes;
- for example, for financial trading and e-commerce use cases.
- BigQuery
- it sits on the edge between data storage and data processing
- use case:
- to use its big data analysis and interactive query and capabilities
- will not use BigQuery,
- for example, as the backings store for an online application.
- Data stored in BigQuery is highly durable.
- Google stores the data in a replicated manner by default and at no additional charge for replicas.
- pay only for the resources you use.
- Data storage in BigQuery is inexpensive.
- Queries incur charges based on the amount of data they process:
- when you submit a query, you pay for the compute nodes only for the duration of that query.
- You don’t have to pay to keep a compute cluster up and running.
- Using BigQuery involves interacting with a number of Google Cloud Platform resources,
- including projects (covered elsewhere in this course), datasets, tables, and jobs.
- Datasets:
- a grouping mechanism that holds zero or more tables.
- the lowest level unit of access control.
- Datasets are owned by GCP projects.
- Each dataset can be shared with individual users.
- Tables:
- A table is a row-column structure that contains actual data.
- Each table has a schema that describes strongly typed columns of values.
- Each table belongs to a dataset.
- Datasets:
- including projects (covered elsewhere in this course), datasets, tables, and jobs.
Relational
Cloud SQL
relational databases
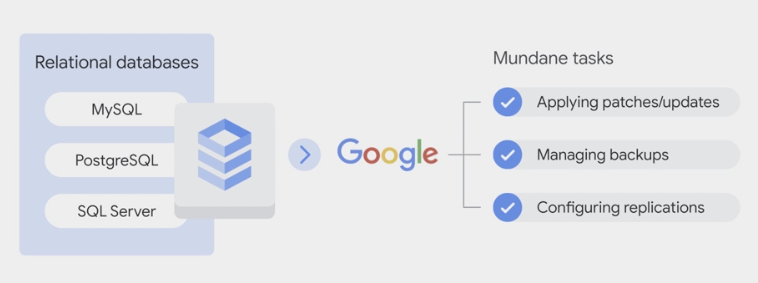
- lot of work to set up, maintain, manage, and administer.
- If that doesn’t sound like a good use of your time but you still want the protections of a relational database, consider Google Cloud SQL
Google Cloud SQL
- run your own database server
- run the database server inside a Compute Engine virtual machine,
- offers choice of the MySQL or PostgreSQL database engines
- a fully managed service.
- capable of handling terabytes of storage.
- If you’re currently using
MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Microsoft SQL Server, then Cloud SQL is your best bet.
benefit of Cloud SQL instances
- automatic replication
- provides several replica services like read, failover, and external replicas.
- if an outage occurs, Cloud SQL can replicate data between multiple zones with automatic failover.
- Cloud SQL backup the data
- either on-demand or scheduled backups.
- It can scale both vertically and horizontally
- vertically by changing the machine type,
- horizontally via read replicas.
- cale up to 128 processor cores, 864 GB of RAM, and 64 TB of storage.
- security perspective
- Cloud SQL instances include network firewalls,
- and customer data is encrypted when on Google’s internal networks, and when stored in database tables, temporary files, and backups.
- control network access
- Cloud SQL instances is accessible by other GCP services and even external services.
- includes a network firewall to control network access to each database instance.
- You can authorize
Compute Engine instancesfor accessCloud SQL instances - and configure the
Cloud SQL instanceto be in the same zone as your virtual machine.
- Cloud SQL also supports other applications and tools
- like SQL WorkBench, Toad,
- and other external applications using standard MySQL drivers.
usecase
- relational databases ideal for online transactional processing
Cloud Spanner
If Cloud SQL does not fit your requirements because you need horizontal scalability, Cloud Spanner.
It offers transactional consistency at a global scale, schemas, SQL, and automatic synchronous replication for high availability.
especially suited for applications that require high availability, strong global consistency, and high input/output operations per second .
it can provide petabytes of capacity.
Cloud Spanner if
- If Cloud SQL does not fit your requirements because you need horizontal scalability
- you have outgrown any relational database, or sharding your databases for throughput high performance, need transactional consistency, global data and strong consistency,
- or just want to consolidate your database.
- Natural use cases include, financial applications, and inventory applications.
NoSQL
Cloud Bigtable
relational database
- use tables
- every row has the same set of columns,
- enforced database schema:
- the database engine, enforces rule and other rules you specify for each table.
- big help for some applications but a huge pain for others.
- Some applications call for a much more flexible approach.
- example
- NoSQL schema.
- for applications that not all the rows might need to have the same columns.
- GCP fully manages the surface
- no need to configure and tune it.
- NoSQL, big data database service.
- databases in Bigtable are sparsely populated tables
- can scale to billions of rows and thousands of columns
- allowing you to store petabytes of data.
- ideal for
- data that has a single lookup key
- Bigtable as a persistent hash table.
- storing large amounts of data with very low latency
- supports high throughput
- both read and write,
- great choice for both operational and analytical applications
- including Internet of Things, user analytics and financial data analysis.
- supports high throughput
- data that has a single lookup key
- Cloud Bigtable is offered through the same open source API as HBase
- HBase: the native database for the Apache Hadoop project.
- having the same API enables portability of applications between HBase and Bigtable.
benefits
- scalability
- compare with own Apache HBase installation,
- manage your own Hbase installation
- scaling past a certain rate of queries per second is going to be tough,
- Bigtable:
- just increase the machine count which doesn’t even require downtime.
- Cloud Bigtable handles administration tasks
- like upgrades and restarts transparently.
- encryption
- All data in Cloud Bigtable is encrypted in both in-flight and at rest.
- use IAM permissions
- to control who has access to Bigtable data.
- Bigtable is the same database that powers many of Google’s core services
- including search, analytics, maps and Gmail.
- Cloud Bigtable is part of the GCP ecosystem, it can interact with other GCP services and third-party clients.
Bigtable Access Patterns
- application API
- streaming
- batch processing
Cloud Datastore
- highly scalable NoSQL database for the applications
- store unstructured objects
- support for
transactions - support for
SQL-like queries. - provides
terabytesof capacity - maximum unit size of one megabyte per entity.
- use cases
- store data from App Engine apps.
- best for semi-structured application data that is used in app engine applications
- free daily quota, separate from any free trials
- build solutions that span App Engine and Compute Engine with Cloud Datastore as the integration point.
- fully-managed service
- automatically handles sharding and replication,
- providing a highly available and durable database
- scales automatically to handle load.
- store data from App Engine apps.
- Unlike Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud Datastore offers transactions that affect multiple database rows
- it lets you do SQL-like queries.
- Cloud Datastore has a free daily quota that provides storage, reads, writes, deletes and small operations at no charge.
Cloud Filestore
NoSQL cloud database for mobile, web, and server development.
Data in Firestore is stored in documents and organized into collections.
Documents can contain complex nested objects and subcollections.
Each document consists of key-value pairs.
Firestore’s NoSQL queries can retrieve specific documents or all documents in a collection that match query parameters.
Queries can include multiple filters and sorting options.
Firestore’s query performance is based on the size of the result set, not the dataset.
Firestore uses data synchronization to update data on connected devices.
It can also efficiently handle simple one-time fetch queries.
Firestore caches data that an app is actively using, allowing it to read, write, listen to, and query data even when offline .
When the device comes back online, Firestore synchronizes any local changes back to the database.
- automatic multi-region data replication, strong consistency guarantees, atomic batch operations, and real transaction
support.
usecase
Firebase Realtime Database
Cloud Memorystore
.

























Comments powered by Disqus.