Confidentiality Attacks
Confidentiality Attacks
Confidentiality Attacks
confidentiality attack: make confidential data viewable by an attacker. (like records, usernames, passwords or e-mails)
Because an attacker often makes a copy of the data, rather than trying to manipulate the data or crash a system, confidentiality attacks often go
undetected.Even if auditing software to track file access were in place, if no one suspected an issue, the audit logs might never be examined.
Example:
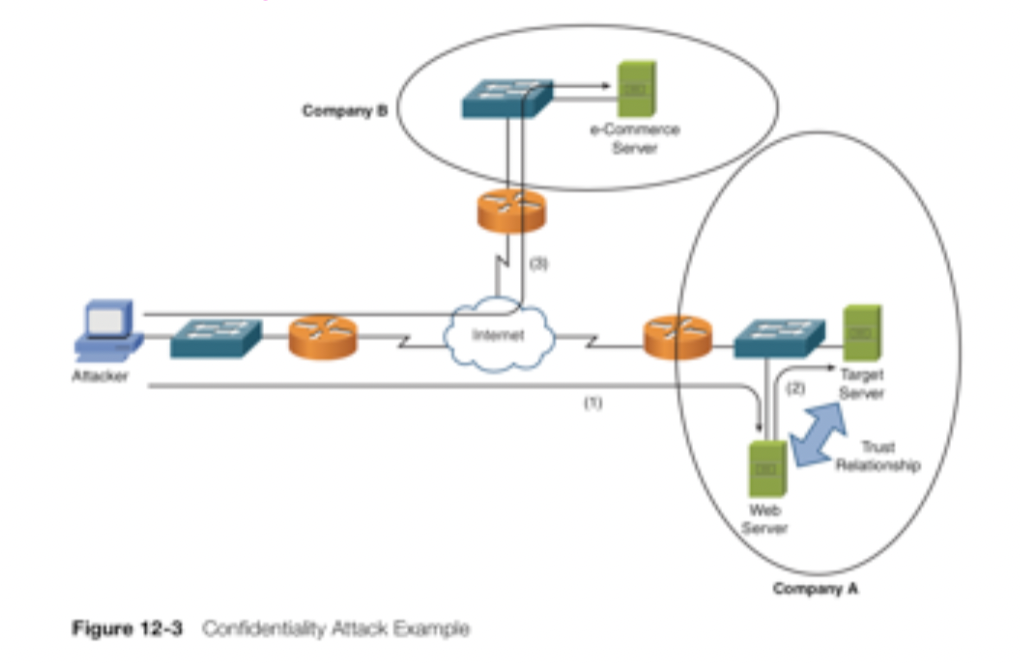
- a
web serverand adatabase serverhave a mutual trust relationship. The database server houses confidential customer information (like customer credit-card information). - As a result,
company Adecided to protect the database server (example, patching known software vulnerabilities) better than the web server. - However, the attacker leverages the trust relationship between the two servers to obtain customer credit-card information and then make a purchase from company B using the stolen credit-card information. The procedure is as follows:
- The attacker
exploits a vulnerabilityin company A’s web server and gains control of it. - The attacker
uses the trust relationshipbetween the web server and the database server to obtain customer credit-card information from the database server. - The attacker
uses the stolen credit-cardinformation to make a purchase from company B.
- The attacker
confidentiality attack methods
Packet capture/sniffing
- Use (like Wireshark), capture packets visible by a PC’s
network interface card (NIC), by placing the NIC inpromiscuous mode. - Some protocols (like Telnet and HTTP) are sent in plain text.
- Therefore, these types of captured packets can be read by an attacker, perhaps allowing the attacker to see confidential information.
Ping sweep / port scan
- A confidentiality attack might begin with a scan of network resources to identify attack targets on a network.
- A ping sweep 扫视;袭击 could be used to
ping a series of IP addresses. - Ping replies might indicate to an attacker that
network resources were reachable at those IP addresses. - After a collection of IP addresses is identified, the attacker might
scan a range of UDP and/or TCP portsto seewhat services are available on the hosts at the specified IP addresses. - Also, port scans often help attackers identify the operating system running on a target system.
Dumpster diving 垃圾装卸卡车
- companies throw away confidential information, without proper shredding,
- some attackers rummage through company dumpsters in hopes of discovering information that could be used to compromise network resources.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) interception
- Because data is often transmitted over wire (like unshielded twisted pair),
- attackers can sometimes copy information traveling over the wire, by intercepting the
electromagnetic interference (EMI)being emitted 发散 by the transmission medium. - These EMI emissions are sometimes called
emanations.
Wiretapping 窃听装置
- If an attacker gains physical access to a wiring closet,
physically tap into telephone cablingto eavesdrop on telephone conversations,insert a shared media hubin-line with a network cable, allowing an attacker to connect to the hub and receive copies of packets flowing through the network cable.
Social engineering
- Attackers sometimes use social techniques to obtain confidential information.
- Example, an attacker might pose as a member of an organization’s IT department and ask a company employee for his login credentials in order for the “IT staff to test the connection.”
Pretexting:- attack based on invented story or pretext.
- Example: answer other’s question to reset password.
Baiting:- using some kind of “gift” as a bait to get someone to install malicious software.
- Example: an attacker could leave a USB, someone pick up and unwittingly install the malicious software.
Quid Pro Quo:- Latin for “something for something.”
- Example:
- one sharing her password in return for his “free” help.
- To increase the chances of succeeding in his attack, use a
voice-over-IP (VoIP) telephone servicethat allows for caller-ID spoofing. Thus, he could supply as his caller-ID the phone number and name of the actual helpdesk for Alice’s company. - This is an instance of another type of attack called
vishing, which is short for VoIP phishing.
Sending information over overt channels 明显的
- An attacker might send/receive confidential information over a network using an overt channel. which can communicate information as a series of codes and/or events.
- example:
tunneling one protocol inside another: like sending instant-messaging traffic via HTTP.Steganography 隐写术: like sending a digital image with millions of pixels, “secret” information encoded in specific pixels, only the sender and the receiver know which pixels represent the encoded information.- binary data could be represented by sending a series of pings to a destination.
- A single ping within a certain period of time could represent a binary 0, while two pings within that same time period represented a binary 1.
FTP bounce
- FTP supports a variety of commands for
setting up a session and managing file transfers. - One of these commands is the
PORTcommand, and it can, in some cases, be used by an attacker to access a system that would otherwise deny the attacker. - Specifically, an attacker connects to an FTP server using the standard port of 21.
- However, FTP uses a secondary connection to send data.
- The client issues a
PORTcommand to specify the destination port and destination IP address for the data transmission. - Normally, the client would send its own IP address and an ephemeral 瞬息的 port number.
- The FTP server would then use a source port of 20 and a destination port specified by the client when sending data to the client.
- However, an attacker might issue a
PORTcommand specifying the IP address of a device they want to access, along with an open port number on that device. - As a result, the targeted device might allow an incoming connection from the FTP server’s IP address, while a connection coming in from the attacker’s IP address would be rejected.
- Fortunately, most modern FTP servers do not accept the
PORTcommand coming from a device that specifies a different IP address than the client’s IP address.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
Comments powered by Disqus.